Dev and Test¶
This document describes the organization of the source code for Interactive and provides instructions on how to build Interactive from source and run tests.
Dev Environment¶
Before building Interactive from the source code, you need to set up a development environment with various dependencies.
Here, we provide two options: installing all dependencies on the local machine or building it within the provided Docker image.
Install Deps on Local¶
Interactive source code should be compatible with and installable on most modern Linux distributions, including Debian, RedHat, and Ubuntu (tested on Ubuntu 22.04), on both x86 and ARM platforms. If you encounter any issues during compilation or installation on your system, please open an issue on our Github Repo.
Note
Interactive currently cannot be compiled from source on macOS, mainly due to some dependencies (seastar) being incompatible with macOS.
To install all dependencies on your local machine, run the following code with the command-line utility script gsctl.py.
python3 gsctl.py install-deps dev
Develop on Docker Container¶
We provided a docker image graphscope-dev with all tools and dependencies included.
docker run -it registry.cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/graphscope/graphscope-dev:latest
Or you can open the codebase of GraphScope in dev container.
Understanding the Codebase¶
Interactive is composed of two parts, the execution engine and frontend compiler.
Interactive Query Engine¶
The Interactive Query Engine code is organized in the flex folder as follows:
codegen: The binarygen_code_from_planis built from this repository, capable of generating C++ code from a physical plan.engines:engines/graph_db: Provides the interface and implementation ofGraphDB, which manages graph storage.engines/hqps_db: Includes the Graph Query Engine implementation, data structures, and physical operators.engines/http_server: Incorporates the HTTP server based on Seastar httpd and defines actors in hiactor.
interactive: Contains product-related components.interactive/docker: Dockerfile for Interactive.interactive/examples: Graph definition examples and raw data.interactive/openapi/openapi_interactive: OpenAPI specification for Interactive’s RESTful API.
storages:storages/metadata: Implementation of the metadata store.storages/immutable_graph: Implementation of immutable graph storage.storages/rt_mutable_graph: Implementation of mutable graph storage based onmutable_csr.
tests: Includes test cases and scripts.third_party: Contains third-party dependencies.utils: Utility classes and functions.
Dependency Graph¶
Interactive follows the lego-like building concept of GraphScope Flex, comprising multiple modules. A dependency graph illustrates the relationships among these modules, although only a subset of third-party dependencies is included for clarity.
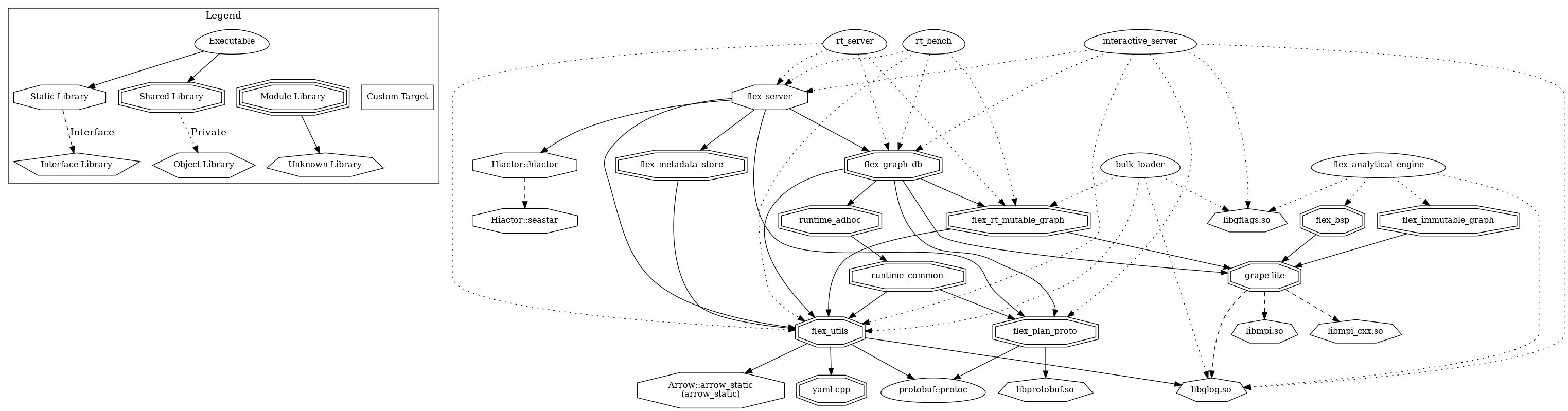
Dependency Graph between modules¶
Compiler¶
The Compiler is crucial in Interactive as it converts graph queries written in graph query languages (Cypher/Gremlin) into physical query plans using GAIA IR.
The Compiler code is found in interactive_engine/compiler.
For additional details on the Compiler, refer to this documentation
Build Interactive¶
First, build the Interactive Query Engine.
git clone https://github.com/alibaba/GraphScope # or replace with your own forked repo
cd GraphScope
git submodule update --init
cd flex
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make -j
Then, build the Compiler.
cd interactive_engine
mvn clean package -DskipTests -Pexperimental
CMake options¶
BUILD_TEST: Indicates whether to build tests.BUILD_DOC: Indicates whether to build Flex documentation.BUILD_ODPS_FRAGMENT_LOADER: Enables support for loading graphs from ODPS tables.USE_PTHASH: Indicates whether to use a perfect hash when building the vertex map.OPTIMIZE_FOR_HOST: Determines if Flex should be optimized for performance on the current machine. Note that enabling this option may result in a binary that does not run on different platforms or CPU architectures.
Testing¶
Numerous test cases have been created for Interactive, which can be referenced in the GitHub workflowinteractive.yaml. Below is a basic test case for validating the accuracy of the SDK and interactive admin service.
Initially, a directory needs to be established as the Interactive workspace, then proceed to create a new graph named modern_graph and import data into the graph.
# Clone the testing data
export GS_TEST_DIR=/tmp/gstest
git clone -b master --single-branch --depth=1 https://github.com/GraphScope/gstest.git ${GS_TEST_DIR}
export GITHUB_WORKSPACE=/path/to/GraphScope
export FLEX_DATA_DIR=${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/flex/interactive/examples/modern_graph
export TMP_INTERACTIVE_WORKSPACE=/tmp/interactive_workspace
cd ${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/flex/build/
# Create interactive workspace
mkdir -p ${TMP_INTERACTIVE_WORKSPACE}
SCHEMA_FILE=${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/flex/interactive/examples/modern_graph/graph.yaml
BULK_LOAD_FILE=${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/flex/interactive/examples/modern_graph/bulk_load.yaml
# Create a directory to put modern_graph's schema.yaml and graph data
mkdir -p ${TMP_INTERACTIVE_WORKSPACE}/data/modern_graph/
cp ${SCHEMA_FILE} ${TMP_INTERACTIVE_WORKSPACE}/data/modern_graph/graph.yaml
# Load data to modern_graph
GLOG_v=10 ./bin/bulk_loader -g ${SCHEMA_FILE} -l ${BULK_LOAD_FILE} -d ${TMP_INTERACTIVE_WORKSPACE}/data/modern_graph/indices/
A workspace is akin to the data directory for a database, housing metadata and graph data. Here is an example.
/tmp/temp_workspace
├── data
│ ├── 1 -> /tmp/temp_workspace/data/modern_graph
│ ├── 2
│ └── modern_graph
└── METADATA
├── GRAPH_META
├── INDICES_LOCK
├── JOB_META
├── PLUGIN_META
├── PLUGINS_LOCK
└── RUNNING_GRAPH
Subsequently, execute the hqps_admin_test.sh script to test the of the interactive admin service.
cd ${GITHUB_WORKSPACE}/flex/tests/hqps
# Change the default_graph field to
bash hqps_admin_test.sh ${TMP_INTERACTIVE_WORKSPACE} ./interactive_config_test.yaml ${GS_TEST_DIR}
The interactive_config_test.yaml specifies the configuration for interactive services.
directories:
workspace: /tmp/interactive_workspace # The workspace to start service on.
log_level: INFO
default_graph: modern_graph # The graph to serve at the beginning
compute_engine:
type: hiactor
workers:
- localhost:10000
thread_num_per_worker: 1
store:
type: cpp-mcsr
metadata_store:
type: file
compiler: # Configurations for the Graph Compiler
planner:
is_on: true
opt: RBO
rules:
- FilterIntoJoinRule
- FilterMatchRule
- NotMatchToAntiJoinRule
meta:
reader:
schema:
uri: http://localhost:7777/v1/service/status
interval: 1000 # ms
statistics:
uri: http://localhost:7777/v1/graph/%s/statistics
interval: 86400000 # ms
endpoint:
default_listen_address: localhost
bolt_connector:
disabled: false
port: 7687
gremlin_connector:
disabled: false
port: 8182
query_timeout: 40000
gremlin_script_language_name: antlr_gremlin_calcite
http_service:
default_listen_address: localhost
admin_port: 7777
query_port: 10000
Starting Service Manually¶
The main entrance for Interactive is interactive_server.
Enable AdminService¶
To start admin service in development, use the command line argument --enable-admin-service true. ${ENGINE_CONFIG} specifies the configuration for interactive query engine, see engine-configuration. ${WORKSPACE} points to the directory where interactive related data is maintaned.
./bin/interactive_server -c ${ENGINE_CONFIG} -w ${WORKSPACE} --enable-admin-service true
Start Compiler Service¶
The Compiler service could be started as a subprocess of the AdminService. This ensures that when switching graphs in the AdminService, the Compiler service also switches to the corresponding graph’s schema. This is the default behavior in the current Interactive.
./bin/interactive_server -c ${ENGINE_CONFIG} -w ${WORKSPACE} --enable-admin-service true --start-compiler true
Error Code¶
Runtime errors are categorized, assigned an error code, and included in the HTTP response body (only for non-200 HTTP responses). The mapping between status codes and HTTP codes is shown in the table below.
Code |
HTTP Code |
|---|---|
OK(0) |
200 |
INVALID_ARGUMENT(2) |
400 |
UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION(11) |
400 |
NOT_FOUND(4) |
404 |
ALREADY_EXISTS(5) |
409 |
PERMISSION_DENIED(8) |
403 |
CODEGEN_ERROR(100) |
500 |
INVALID_SCHEMA(101) |
400 |
ILLEGAL_OPERATION(102) |
400 |
INTERNAL_ERROR(103) |
500 |
INVALID_IMPORT_FILE(104) |
400 |
IO_ERROR(105) |
500 |
QUERY_FAILED(106) |
500 |
default |
500 |